ASCA's Solid-state Imaging Spectrometers
The construction of ASCA's two Solid-state Imaging Spectrometers (SIS) was a joint effort of MIT, ISAS and Osaka University. Each SIS camera is based around four, 420x422 square pixel CCD chips, abutted side-by-side, front-side illuminated, operated in frame-store configuration.
The "vital statistics" of the SIS are as follows:
- Energy Range: 0.4 keV to 10 keV keV
- Energy Resolution: 2 percent at 5.9 keV
- Field of View: 22 by 22 arcmin square
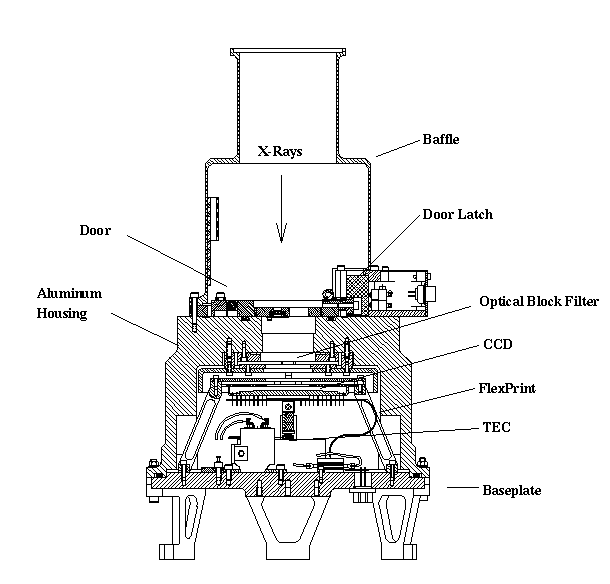
Cross section of SIS (figure was taken from K.C.Gendreau's thesis).


Left:Four individual CCDs are combined in a single package to make a single SIS focal plane (figure was taken from K.C.Gendreau's thesis). Right:Configuration of the two SIS on the ASCA focal plane.
More SIS Information
- SIS news
- SIS calibration data
- Important events on SIS during the ASCA mission
- SIS articles in the ASCA newsletter:
- vol. 1 Overview and Current Status of the ASCA SIS
- vol. 2 SIS background
- vol. 2 SIS Long Term Performance
- vol. 2 SIS DFE and Echo
- vol. 3 Effects of radiation damage on SIS performance
- vol. 4 SIS Calibration and Software
- vol. 4 SIS Grad 6 Events
- vol. 4 Effects of the Flickering Pixels to the SIS Background
References: Keith C. Gendreau's doctoral thesis (1995, MIT), "X-Ray CCD Calibration; X-Ray CCD Radiation Damage Evaluation and Modeling; Use of CCDs to Measure the Spectrum of the Cosmic X-Ray Backgrounds with ASCA"
If you have any questions concerning ASCA, visit our Feedback form.

