MCG-6-30-15
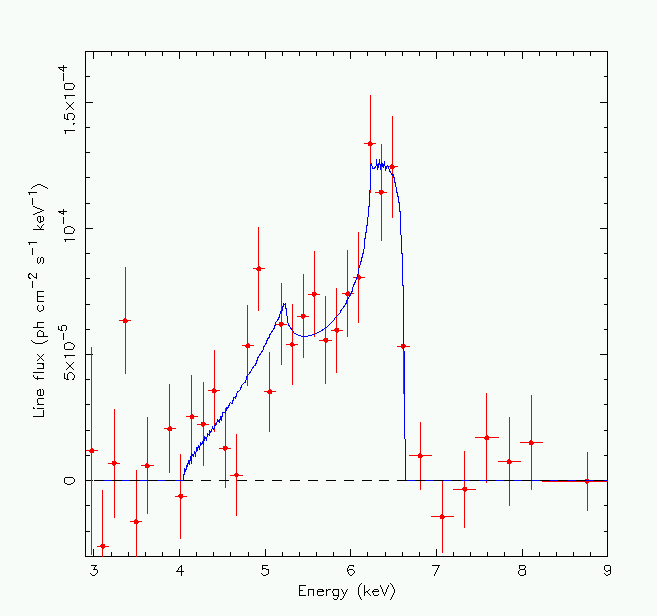
Image Credit: Tanaka et al., Copyright: Nature, 375, 659, 1995
Image generated by Dr. Paul Nandra NASA/GSFC
The line profile of iron K-alpha from MCG-6-30-15 observed by the ASCA
satellite (Tanaka et al, 1995, Nature, 375, 659). The emission line is
extremely broad, with a width indicating velocities of order one-third
of the speed of light. There is a marked asymmetry towards energies
lower than the rest-energy of the emission line (6.4 keV). This
asymmetry is most likely caused by gravitational and
relativistic-Doppler shifts near the black hole
at the center of the galaxy. The solid line shows the model profile expected from a
disk of matter orbiting the hole, extending between 3 and 10
Schwarzschild radii.
Get the Color Postscript image. of this spectrum.
For more information see:
"On the dependence of iron K-line profiles with luminosity in Active Galactic Nuclei"; Nandra, K., Mushotzky, R.F., George, I.M., Turner, T.J. , Yaqoob, T. 1997, ApJ, 488, L91
There is also a simulation of a black hole that may explain this result.
This file was last modified on Wednesday, 16-Feb-2005 12:04:47 EST
Curator:
HEASARC Guest Observer Facility
If you have any questions concerning ASCA, visit our Feedback form.

