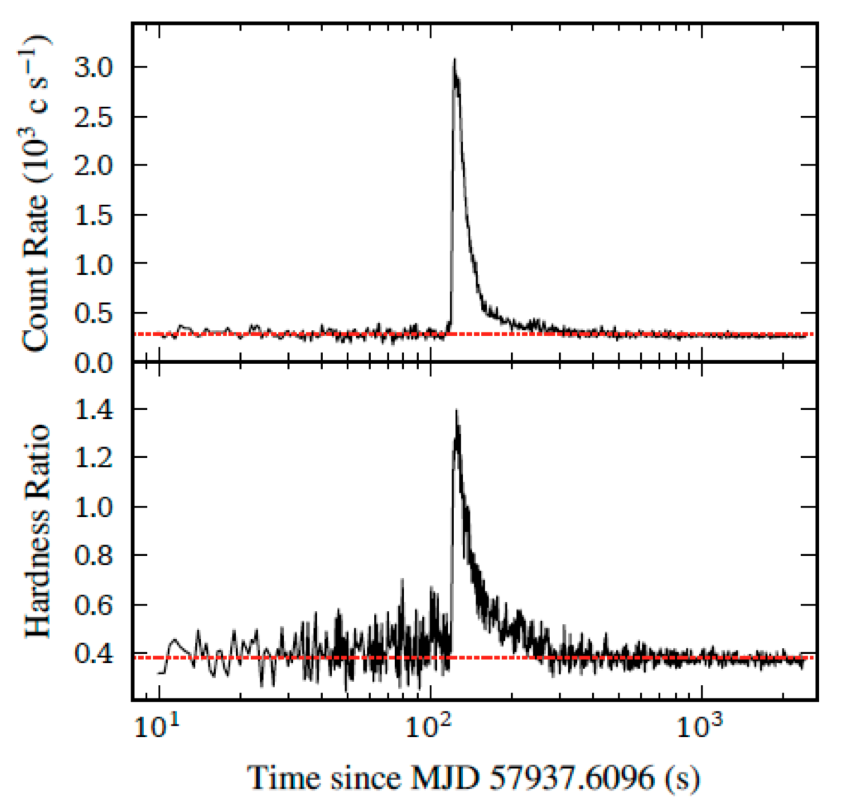
NICER / ISS Science Nugget for February 22, 2018First refereed paper using NICER data published in the Astrophysical JournalThe first peer reviewed paper out of NICER has been accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, where it will be included in a Focus Issue on early NICER science results. Its title is "NICER OBSERVES THE EFFECTS OF AN X-RAY BURST ON THE ACCRETION ENVIRONMENT IN AQL X-1" by L. Keek et al. The abstract is below: Accretion disks around neutron stars regularly undergo sudden strong irradiation by Type I X-ray bursts powered by unstable thermonuclear burning on the stellar surface. We investigate the impact on the disk during one of the first X-ray burst observations with the Neutron Star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) on the International Space Station. The burst is seen from Aql X-1 during the hard spectral state. In addition to thermal emission from the neutron star, the burst spectrum exhibits an excess of soft X-ray photons below 1 keV, where NICER's sensitivity peaks. We interpret the excess as a combination of reprocessing by the strongly photoionized disk and enhancement of the pre-burst persistent flux, possibly due to Poynting-Robertson drag or coronal reprocessing. This is the first such detection for a short sub-Eddington burst. As these bursts are observed frequently, NICER will be able to study how X-ray bursts affect the disk and corona for a range of accreting neutron star systems and disk states.The Figure shows the burst observed by NICER that supported this analysis.
NICER
|