
 Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/A.Siemiginowska (CfA) & J.Bechtold (U. Arizona); Radio: Siemiginowska et al. (VLA)
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/A.Siemiginowska (CfA) & J.Bechtold (U. Arizona); Radio: Siemiginowska et al. (VLA)
Ins and Outs of Black Holes
Somehow infall of material often produces large collimated outflows. This
is exemplified in active galaxies, where large clouds of gas and, possibly
stars and planets fall onto a black hole at the center of the galaxy, and
producing an enormous jet of material which can be millions of light years
long. Such jets are often called radio jets, since most were discovered
using extremely high resolution observations with radio telescopes. The
radio emission arises from relatively cool material inside the jet. Now
high resolution X-ray images obtainable with the Chandra X-ray observatory show
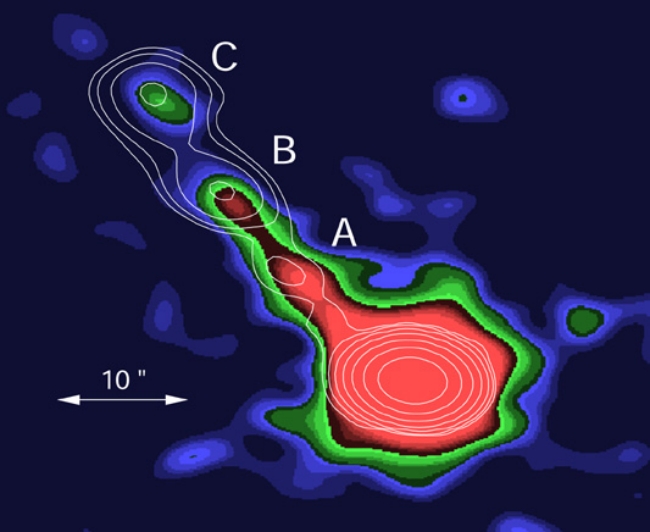
astronomers that radio jets are often X-ray bright, too. The image above
shows a false-color X-ray image of the
active galaxy PKS1127-145 obtained by Chandra. The bright central
source is thought to be emission from a supermassive black hole; the X-ray
jet stretches to the upper left of the image. The white lines are the
contours of the radio jet, and show that the X-ray emitting and radio
emitting material exist together in the jet. At the distance of
PKS1127-145, this jet is about 1 million lightyears long. Interestingly
astronomers have found that the emission from the core of the galaxy is absorbed by
certain atoms in a galaxy between us and PKS1127-145; by measuring the
amount of absorption astronomers can deduce the amount of chemical
evolution in the intervening galaxy.
Last Week *
HEA Dictionary * Archive
* Search HEAPOW
* Education
Each week the HEASARC
brings you new, exciting and beautiful images from X-ray and Gamma ray
astronomy. Check back each week and be sure to check out the HEAPOW archive!
Page Author: Dr. Michael F.
Corcoran
Last modified February 11, 2002


