
 Credit: ESA
Credit: ESA
Hot Light in the Stellar Nursery: The View from
XMM-Newton
The Large Magellanic Cloud is a small irregular galaxy in orbit around the
Milky Way. This galaxy is full of gas and dust, the raw materials out of
which stars form, and is a site of active star formation, and frequent
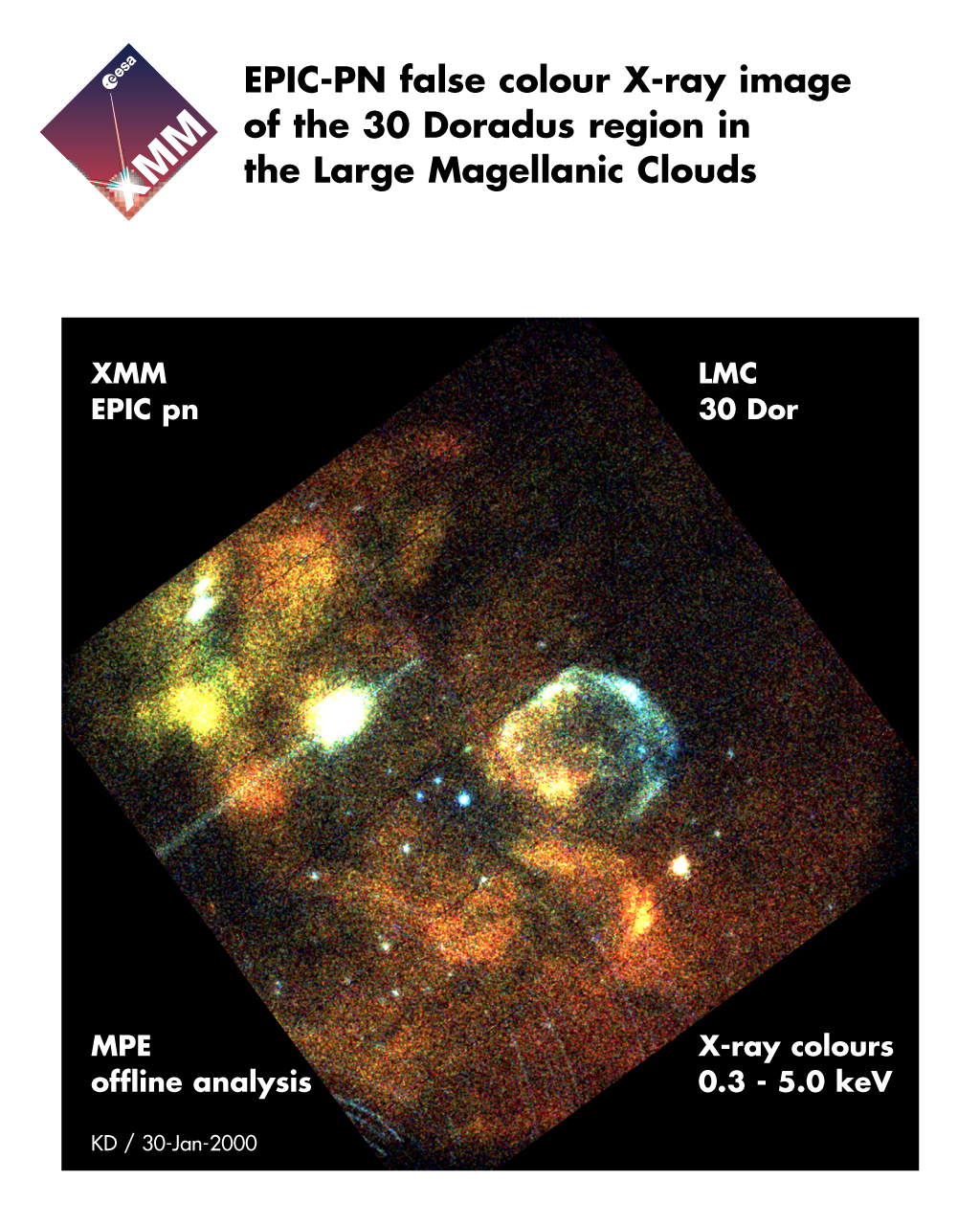
stellar death. The image above captures an image of extremely hot gas in
one location of the LMC, the Tarantula Nebula, also known as the 30 Doradus
Nebula, and reveals the full range of the life cycle of stars, from birth
to death. This X-ray colour image, made with the EPIC camera on the
XMM-Newton X-ray telescope
shows spherical bubbles of hot gas produced by stellar explosions which are
releasing newly manufactured elements into the Tarantula Nebula, and
X-rays from newly formed, highly active young stars. The image is made so
as to reveal the temperature of the X-ray emitting gas: blue
indicating the hottest regions, green the intermediate temperatures and red
the coldest regions (in X-ray speak, cold means temperatures of "only" 1
million degrees!). Most of the blue X-rays have never been observed
this XMM-Newton observation.
Last Week *
HEA Dictionary * Archive
* Search HEAPOW
* Education
Each week the HEASARC
brings you new, exciting and beautiful images from X-ray and Gamma ray
astronomy. Check back each week and be sure to check out the HEAPOW archive!
Page Author: Dr. Michael F.
Corcoran
Last modified June 14, 2001


