
 Credit: N. White (HEASARC) and W. Cash (U. Colorado)
Credit: N. White (HEASARC) and W. Cash (U. Colorado)
Witness to the End of Time
In the last year of the millenium, did you ever expect to witness the end
of time? If NASA's plans succeed, this should be possible early in the
next millenium, by obtaining a picture of the "event horizon" of a black
hole. Black holes are unusual regions of space surrounding a
"singularity", a point in space of infinite density. The event horizon is
a theoretical surface which surrounds the singularity, dividing the
"inside" of the black hole from the "outside": inside the event horizon,
nothing can escape from the black hole or communicate information to the
rest of the universe. Einstein's general
theory of relativity predicts that, as the event horizon is approached,
time slows down; at the event horizon, time comes to a standstill.
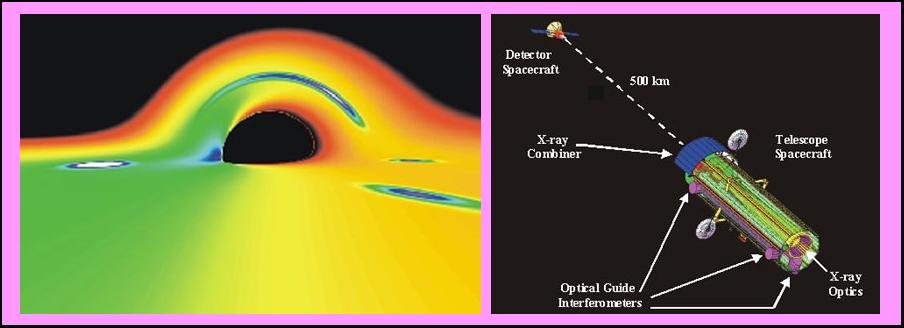
MAXIM, the Micro-Arcsecond X-ray
Imaging Mission, is a proposed NASA space observatory designed to obtain
super-high spatial resolution images. If successful, this observatory will
allow us to view the region in space very near the event horizon, to, in
effect, "take a picture" of a black hole. This mission will use a new
technique called X-ray interferometry, in which images from a set of widely
separated telescopes are combined to produce images of incredibly fine
detail. A preliminary version of MAXIM, called the MAXIM Pathfinder, is
shown above right. The image in the upper left is our best guess of what a
black hole will look like to MAXIM. This simulated image shows a disk of
material swirling into the event horizon; the flat disk is apparently bent
by the strong gravity near the black hole. As the material falls onto the
event horizon, it radiates strongly in X-rays. MAXIM is designed to image
these X-rays and so allow us to study material down to the black hole's
surface.
Last Week *
HEA Dictionary * Archive
* Search HEAPOW
* Education
Each week the HEASARC
brings you new, exciting and beautiful images from X-ray and Gamma ray
astronomy. Check back each week and be sure to check out the HEAPOW archive!
Page Author: Dr. Michael F.
Corcoran
Last modified May 26, 2001


