
 Credit: ESA media relations, media@esa.int (Top); Piersanti, M., et al. Nat Commun 14, 7013 (2023; bottom)
Credit: ESA media relations, media@esa.int (Top); Piersanti, M., et al. Nat Commun 14, 7013 (2023; bottom)
A Disturbance in the Force
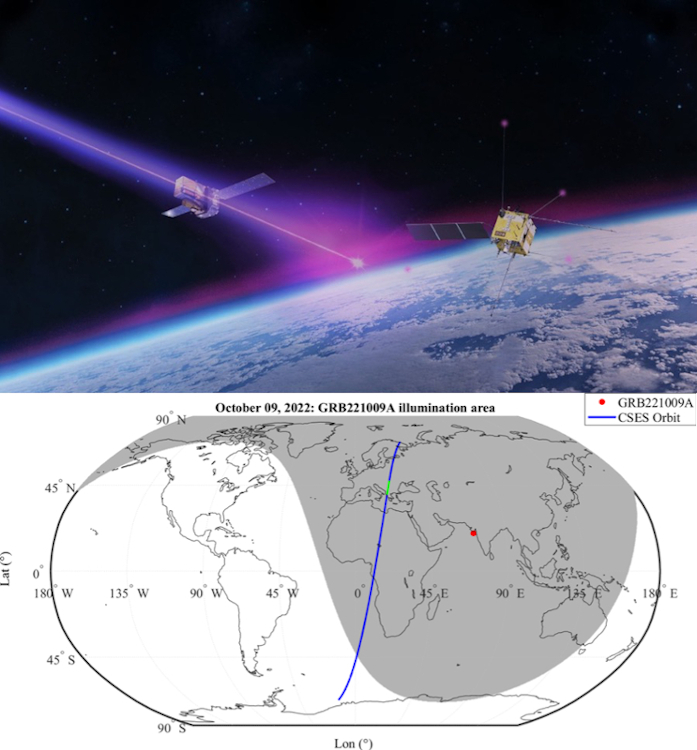
The gamma-ray burst which occurred on October 9, 2022 (and known to scientists as GRB221009a, sometimes called the "BOAT", short for "brightest of all time") was an extraodinary event. This burst, produced by the collapse and death of a massive star leading to the formation of a black hole, was the brightest such burst ever recorded - so bright, in fact, that another similarly bright gamma-ray outburst is not expected for 10,000 years. This burst was detected by an entire fleet of orbiting high-energy observatories (like INTEGRAL, the Neil Gehrels Swift observatory, and the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, to name just a few). The top image above shows an illustration of radiation from the burst traversing the cosmos and being detected by INTEGRAL. It turns out that the high-energy emission from GRB 221009a was so bright that even earth's ionosphere felt its impact. The ionosphere is the upper part of earth's atmosphere, extending from about 50 to 1000 km above earth's surface, where solar radiation strips electrons from atoms, turning them into electrically charged particles, or ions. The state of the ionosphere plays an important role in determining the "space weather" conditions affecting satellites, and the International Space Station, in orbit around the earth. The bottom part of the picture shows the orbital track of the China Seismo-Electromagnetic Satellite (CSES), a satellite designed to monitor the electrical state of the ionosphere to see if ionospheric changes may be correlated with intense earthquakes on the ground. On October 9, 2022, at the exact time of the BOAT burst, the CSES satellite, in the region of its orbit marked in green, measured a large, sudden change in the electrical state of the ionosphere, at an altitude of 500 km. This shows that cosmic explosions, even extragalactic ones like the BOAT, can have a significant impact on earth - and further indicates the potentially devastating effects that a supernove in the Milky Way might have for life on earth.
Published: December 11, 2023
<
HEA Dictionary ● Archive
● Search HEAPOW
● Other Languages
● HEAPOW on Facebook
● Download all Images
● Education ● HEAD
>

Each week the HEASARC
brings you new, exciting and beautiful images from X-ray and Gamma ray
astronomy. Check back each week and be sure to check out the HEAPOW archive!
Page Author: Dr. Michael F. Corcoran
Last modified Tuesday, 27-Feb-2024 10:15:16 EST


