Supernova Remnant VRO 42.05.01
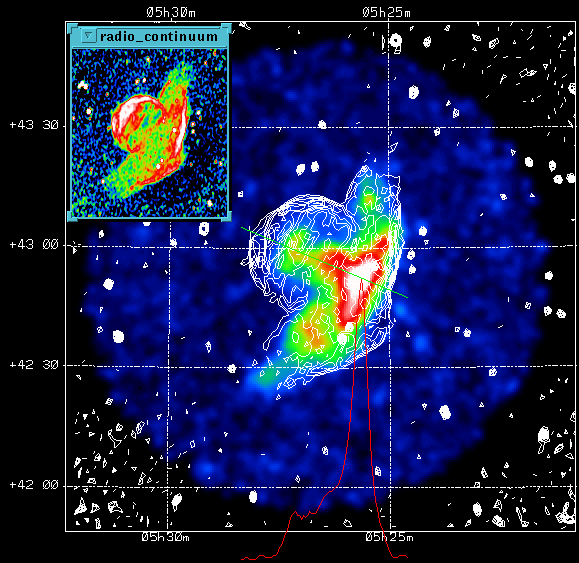
ROSAT PSPC image (from Burrows and Guo, ApJ, 421, L19, 1994 ) of the galactic supernova remnant (SNR) VRO 42.05.01 (also known by its galactic coordinates as G166.0+4.3). The ROSAT image, shown in false color representation, includes X-rays between about 0.5 keV and 2 keV which are believed to be produced by emission from hot gas (T ~ 8.5 million degrees Celsius) in the interior of the supernova remnant. The radio continuum image shown in the inset (from Dr. T. Landecker of the Dominion Radio Astronomy Observatory) is overlaid on the X-ray image as contour lines, showing that X-ray emission fills the interior of the radio shell, although the SNR looks very different at these two wavelengths. The radio image has a typical edge-brightened appearance, while the X-ray image is brightest in the interior and relatively faint at the edges. The intensity profile along the line shown in green, which roughly bisects the SNR along its symmetry axis, is shown in red along the bottom of the image, and has a very sharp peak in intensity in the white portion of the color image. This bright spot may be due to increased X-ray emission as the shock wave from the supernova explosion devours an interstellar cloud. The peculiar morphology of this SNR is believed to result from the eruption of a spherical SNR (the upper left portion) into a region of very low density. The SNR then expanded rapidly into this low density cavity in the interstellar medium, producing the larger "wing" component in the lower right-hand half of the image.
This work was done by Dr. David Burrows and graduate student Zhiyu Guo of the Penn State Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics.
![]() Link to Dr. David Burrows'
X-ray shadows page.
Link to Dr. David Burrows'
X-ray shadows page.
Curator:
HEASARC Guest Observer Facility
Please use the Feedback link if you have questions on ROSAT.

