THE XMM-NEWTON MIRRORS
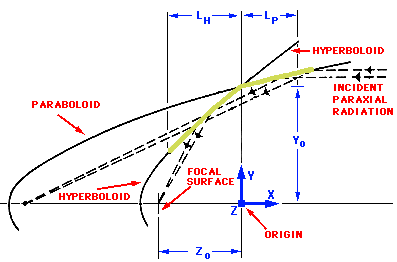
Mirrors for X-ray telescopes are built in a manner very different from those of optical telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. Instead of reflection angles near 180 degrees, X-ray mirrors only deflect the photons by a few degrees, as shown in the inset in the lower figure above (the upper figure shows an expanded view of the geometry). The combination of a reflection off the first paraboloid surface with a second reflection off the hyperboloid surface will focus the X-rays on the focal plane. This is the geometry of the Wolter Type I mirror system.
| Mirror Module Details | |
|---|---|
| Mirror Type | Wolter Type 1 |
| Focal Length | 7500 mm |
| Outermost Mirror Radius | 350 mm |
| Innermost Mirror Radius | 159 mm |
| Axial Mirror Length (paraboloid + hyperboloid) | 600 mm |
| Outer Mirror Wall Thickness | 1.07 mm |
| Inner Mirror Wall Thickness | 0.47 mm |
| Minimum Packing Distance | 3 mm |
| Reflective Surface | Gold |
| Mirror Substrate | Monolithic Nickel |
| Number of Mirrors (paraboloid + hyperboloid) | 58 |
| Mirror Module Mass | 437 kg |
| Angular Resolution, Half Energy Width | 15 arc seconds, 0.1-10 keV |
| Angular Resolution, Full Width Half Maximum | <6 arc seconds, 0.1-10 keV |
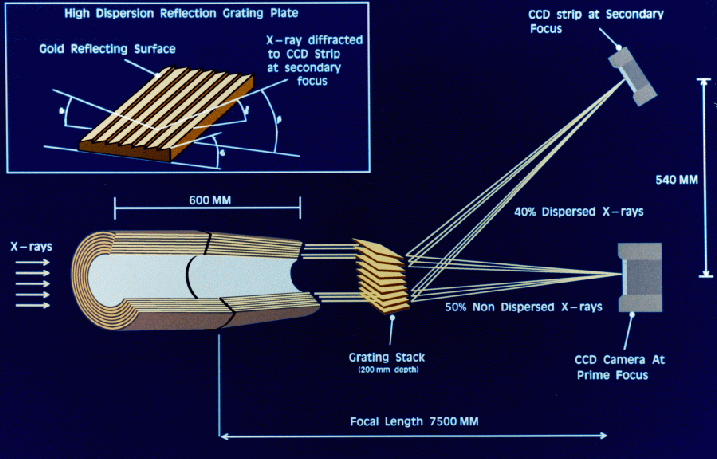
The above figure shows the geometry for the RGS. The gratings of the Reflection Grating Assembly sit in the light paths between the mirrors and the EPIC MOS cameras. They deflect about 40% of the light to the RGS Focal Cameras and allow about 42% of the light to continue on to EPIC. The rest of the light is absorbed by the support structures.
If you have any questions concerning XMM-Newton send email to xmmhelp@athena.gsfc.nasa.gov



