Hydra Cluster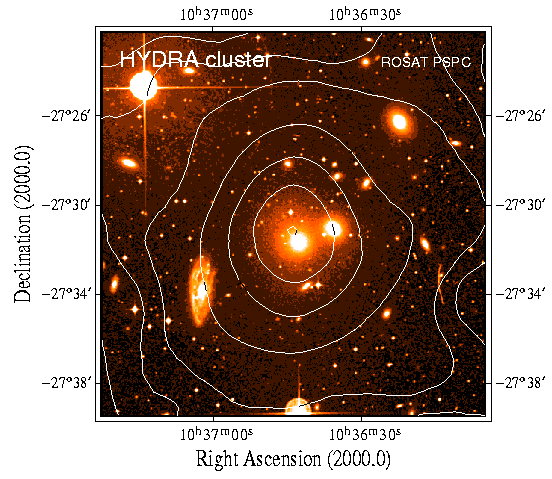 (Image and Text Credit: ROSAT/MPE) ROSAT observation of the galaxy cluster in the constellation Hydra. The X-ray intensity map taken with ROSAT is superposed onto the optical image of the central part of the cluster. The maximum of the X-ray emission coincides with the position of the two brightest elliptical galaxies at the center of the cluster. With a distance of approximately 200 million light years and a mass of nearly 4 x 1015 solar masses this galaxy cluster contributes to the gravitational attraction of the so-called Great Attractor.
IMAGES |
By Mission |
Stars |
HEASARC Home | Observatories | Archive | Calibration | Software | Tools | Students/Teachers/Public Last modified: Thursday, 26-Jun-2003 13:48:46 EDT |

