


Next: Point Source Sensitivity
Up: FEASIBILITY: XMA + HRI
Previous: FEASIBILITY: XMA + HRI
In order to estimate the HRI
response to a cosmic X-ray source, several performance characteristics of
the combined HRI and ROSAT telescope are needed. In the sections that
follow we provide estimates of minimum source count rate detection and
expected count rates from sources. The assumptions that were used in
providing these estimates are:
- The HRI/Telescope effective area is that shown in
Figure 11.1
 and listed in Table 11.1
and listed in Table 11.1  . The effective
area is the product of the XMA area, the transmission of the Filter and
Shield of the HRI, and the CsI coated MCP quantum efficiency.
. The effective
area is the product of the XMA area, the transmission of the Filter and
Shield of the HRI, and the CsI coated MCP quantum efficiency. - The HRI point source detection cell size is 5'' on a
side. This is based on the combination of the XMA point spread function,
the HRI detector resolution, and the estimated aspect uncertainty. The
aspect uncertainty is the largest contributor to the choice of detection
cell size and it remains an estimate at this time.
- 50 percent of the source photons fall within the detection cell. We have
used the half power point for the mirror of 3'' diameter and
the aspect smearing to make this estimate. It is likely to be conservative.
- The HRI internal background rate is about 1.5 counts s
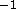 . This
background is mainly due to radioactive isotopes in the MCP glass.
. This
background is mainly due to radioactive isotopes in the MCP glass. - The HRI external background from trapped particles,cosmic rays, and
solar x-rays varies with the orbital position and viewing direction. As
discussed in § 7.8.3
 the typical ROSAT rate is
about 3.0 counts s
the typical ROSAT rate is
about 3.0 counts s 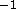 , but may be as much as 3 to 4 times greater
for short intervals of an observation.
, but may be as much as 3 to 4 times greater
for short intervals of an observation. - The X-ray background is computed from the spectrum shown in
Figure 11.2
 ,
which is a compilation of Wisconsin and LLL measurements (ApJ 193, L133
and 172, L67) of the diffuse galactic background, and an extrapolation
of a power law fit to the extragalactic background (e.g., Schwartz 1978
IAU/COSPAR Proceedings). In estimating the HRI count rate we integrate
this spectrum over the total effective area of the XMA + HRI. We note
that the Filter and Shield greatly reduce the HRI sensitivity at low
energies and that there is a major dip in effective area at the carbon
edge. It should also be noted that the galactic component of the x-ray
background varies with the viewing direction. We have taken a
conservative estimate of the galactic background in the sense that we
use the high emission estimates in calculating the HRI count rates. In
some cases the HRI background count rates due to galactic emission may
be up to a factor of 5 lower than the value of 1.0 counts s
,
which is a compilation of Wisconsin and LLL measurements (ApJ 193, L133
and 172, L67) of the diffuse galactic background, and an extrapolation
of a power law fit to the extragalactic background (e.g., Schwartz 1978
IAU/COSPAR Proceedings). In estimating the HRI count rate we integrate
this spectrum over the total effective area of the XMA + HRI. We note
that the Filter and Shield greatly reduce the HRI sensitivity at low
energies and that there is a major dip in effective area at the carbon
edge. It should also be noted that the galactic component of the x-ray
background varies with the viewing direction. We have taken a
conservative estimate of the galactic background in the sense that we
use the high emission estimates in calculating the HRI count rates. In
some cases the HRI background count rates due to galactic emission may
be up to a factor of 5 lower than the value of 1.0 counts s 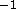 used here.
used here.
|
Energy | Lambda | Effective | Energy | Lambda | Effective |
|
(keV) | (Å) | Area (cm  ) ) | (keV) | (Å) | Area (cm  ) ) |
| 0.10 | 124.0 | 1.0 | 1.10 | 11.3 | 94.5 |
|
0.20 | 62.0 | 20.2 | 1.20 | 10.3 | 89.7 |
|
0.28 | 44.3 | 43.5 | 1.30 | 9.5 | 84.7 |
|
0.28 | 44.1 | 0.0 | 1.40 | 8.9 | 76.1 |
|
0.30 | 41.3 | 1.0 | 1.50 | 8.3 | 56.5 |
|
0.40 | 31.0 | 10.6 | 1.60 | 7.8 | 50.0 |
|
0.50 | 24.8 | 19.3 | 1.70 | 7.3 | 37.2 |
|
0.60 | 20.7 | 7.6 | 1.80 | 6.9 | 28.0 |
|
0.63 | 19.7 | 11.9 | 1.90 | 6.5 | 19.4 |
|
0.70 | 17.7 | 35.5 | 2.00 | 6.2 | 11.2 |
|
0.80 | 15.5 | 59.9 | 2.10 | 5.9 | 2.7 |
|
0.90 | 13.8 | 82.6 | 2.20 | 5.6 | 0.6 |
|
1.00 | 12.4 | 83.2 | 2.30 | 5.4 | 0.4 |
|
| | | 3.40 | 5.2 | 0.2 |
Table: 11.1
ROSAT XMA+HRI Effective Area
None of these assumptions is absolutely correct, but they provide a
typical description of the XMA+HRI performance which may be useful
in preparing ROSAT observation proposals.



Next: Point Source Sensitivity
Up: FEASIBILITY: XMA + HRI
Previous: FEASIBILITY: XMA + HRI
Michael Arida
Tue Jun 11 16:18:41 EDT 1996
 and listed in Table 11.1
and listed in Table 11.1  . The effective
area is the product of the XMA area, the transmission of the Filter and
Shield of the HRI, and the CsI coated MCP quantum efficiency.
. The effective
area is the product of the XMA area, the transmission of the Filter and
Shield of the HRI, and the CsI coated MCP quantum efficiency. the typical ROSAT rate is
about 3.0 counts s
the typical ROSAT rate is
about 3.0 counts s  ,
which is a compilation of Wisconsin and LLL measurements (ApJ 193, L133
and 172, L67) of the diffuse galactic background, and an extrapolation
of a power law fit to the extragalactic background (e.g., Schwartz 1978
IAU/COSPAR Proceedings). In estimating the HRI count rate we integrate
this spectrum over the total effective area of the XMA + HRI. We note
that the Filter and Shield greatly reduce the HRI sensitivity at low
energies and that there is a major dip in effective area at the carbon
edge. It should also be noted that the galactic component of the x-ray
background varies with the viewing direction. We have taken a
conservative estimate of the galactic background in the sense that we
use the high emission estimates in calculating the HRI count rates. In
some cases the HRI background count rates due to galactic emission may
be up to a factor of 5 lower than the value of 1.0 counts s
,
which is a compilation of Wisconsin and LLL measurements (ApJ 193, L133
and 172, L67) of the diffuse galactic background, and an extrapolation
of a power law fit to the extragalactic background (e.g., Schwartz 1978
IAU/COSPAR Proceedings). In estimating the HRI count rate we integrate
this spectrum over the total effective area of the XMA + HRI. We note
that the Filter and Shield greatly reduce the HRI sensitivity at low
energies and that there is a major dip in effective area at the carbon
edge. It should also be noted that the galactic component of the x-ray
background varies with the viewing direction. We have taken a
conservative estimate of the galactic background in the sense that we
use the high emission estimates in calculating the HRI count rates. In
some cases the HRI background count rates due to galactic emission may
be up to a factor of 5 lower than the value of 1.0 counts s