| About ROSAT |
ROSAT Home Page | ROSAT Images |
|---|
The minimum detectable count rate for the PSPC depends on the background
count rate and the effective size of an unresolved source (i.e., it depends
on the off-axis angle). The minimum detectable count rate, ![]() ,
can be estimated from the formula:
,
can be estimated from the formula:
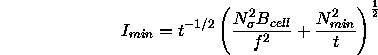
where ![]() is the required significance threshold (i.e., signal-to-noise),
is the required significance threshold (i.e., signal-to-noise),
![]() is the background count rate in the ``detection cell'', f is
the fraction of the total source count included in
the ``detection cell'',
is the background count rate in the ``detection cell'', f is
the fraction of the total source count included in
the ``detection cell'', ![]() is
the minimum number of photons required to
constitute a detection and t is the integration time.
is
the minimum number of photons required to
constitute a detection and t is the integration time.
Note that the effective point response function
of the PSPC depends on energy (cf., § 4.2.2  ) and hence on
the spectrum of the considered source as well as the position of the
source in the field of view. For the sensitivity calculations
a circular detection cell of
) and hence on
the spectrum of the considered source as well as the position of the
source in the field of view. For the sensitivity calculations
a circular detection cell of ![]() radius, an
radius, an
![]() percent fraction of all source photons in the detect cell,
a
percent fraction of all source photons in the detect cell,
a ![]() confidence level of detection as well as a minimum
of number of 10 counts per source have been assumed.
Because the PSPC background depends sensitively on energy
(cf., § 7.8.2
confidence level of detection as well as a minimum
of number of 10 counts per source have been assumed.
Because the PSPC background depends sensitively on energy
(cf., § 7.8.2  ), two sets of calculations are given, one
applicable to the total band (0.1 - 2.4 keV), the other to the
hard band (0.4 - 2.4 keV) only, where the overall background is
significantly reduced. In Figure 10.1
), two sets of calculations are given, one
applicable to the total band (0.1 - 2.4 keV), the other to the
hard band (0.4 - 2.4 keV) only, where the overall background is
significantly reduced. In Figure 10.1  ,
the minimum detectable PSPC count rate is plotted as a
function of exposure time for a low, medium and high level of
mean detector background in the total band and hard band respectively.
As is obvious from Figure 10.1
,
the minimum detectable PSPC count rate is plotted as a
function of exposure time for a low, medium and high level of
mean detector background in the total band and hard band respectively.
As is obvious from Figure 10.1  the PSPC becomes background-limited for exposure times around
10 ks depending on the background level (and the chosen detection cell
size). However, the transition between the photon- and background
limited regime is rather smooth; note that Figure 10.1
the PSPC becomes background-limited for exposure times around
10 ks depending on the background level (and the chosen detection cell
size). However, the transition between the photon- and background
limited regime is rather smooth; note that Figure 10.1  only applies to on-axis observations, for off-axis observations larger detect
cell sizes and consequently larger background values must be used.
only applies to on-axis observations, for off-axis observations larger detect
cell sizes and consequently larger background values must be used.