Subsections
2. Updates and Ongoing Issues
2.1 Introduction
This chapter contains information on current caveats and things to watch out for
when working with XRISM data.
Please also check the XRISM web page, which is updated more frequently than this guide, for the latest on newly identified issues or solution to previously identified issues.
2.2 Latest Changes and Updates
- 2024 August: XRISM software was included in HEASoft (version 6.34). First XRISM CALDB, version 240815, was released.
2.3 Ongoing Issues
Resolve
- We recommend using Hp events only for spectral analysis
because the Hp and Mp events currently have significant gain inconsistencies: merging
these two event grades degrades spectral resolution significantly.
We expect this issue to be resolved in a near-future update of the software.
- Pixel 27 shows somewhat irregular gain variation.
We recommend not using the data for scientific analyses.
- The onboard calibration found more Ls events than expected from the ground study.
The so-called anomalous Ls events do not originate from direct X-ray signals from celestial objects, but the current analysis scheme assumes so.
The item "Removing Ls Events from Cleaned Event Files" in Section 6.3 shows a measure to mitigate this problem for relatively weak sources.
The studies for bright sources are underway.
Xtend
- Cosmic ray echo events produce false events at affected pixels
at every exposure frame until a daily dark-level initialization.
These events show multiple
high-count dots in Xtend images.
Software released in the near future will efficiently remove these events.
For now, we suggest that users avoid analyzing data below
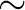 0.6 keV or
running the HEASoft tool searchflickpix with special parameters to remove the events.
0.6 keV or
running the HEASoft tool searchflickpix with special parameters to remove the events.
- The Xtend housing blocks the light path near the Xtend FOV edge on CCD_ID=2 (see Figure 6.2 on POG). The current calibration does not include this effective area reduction, causing flux underestimates of sources detected in this tiny area.
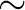 0.6 keV or
running the HEASoft tool searchflickpix with special parameters to remove the events.
0.6 keV or
running the HEASoft tool searchflickpix with special parameters to remove the events.