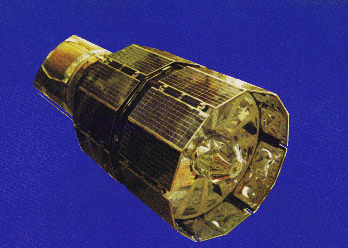
ESRO 2B
Launched on 17 May 1968, ESRO-2B had an elliptical orbit with (initially)
apogee 1086 km, perigee 326 km, and inclination 97.2 degrees. The orbital
period was 98.9 minutes. It was the first successful ESRO satellite launch.
ESRO (European Space Research Organisation), was the forerunner of ESA.
ESRO-2B was also known as Iris. The satellite was mainly intended to study
X-ray and particle emissions from the Sun, however, it is credited with some
extra-solar observations. The spacecraft was cylindrical in shape, with a
0.76 m diameter and a 0.85 m height. It weighed 80 kg. The failure of
the on-board tape recorder in December 1968 (after roughly 6.5 months
of operation) was catastrophic for the 2 X-ray experiments. They
did not provide any significant data return after that time. The
satellite reentered the atmosphere on 8 May 1971. | |||||||||||||||||
| Experiments | |
|---|---|
| S25 | Time variations on radiation belt population |
| S27 | Solar and radiation belt protons and alpha particles, protons in energy range 1-100 MeV |
| S28 | High-energy solar protons and alpha particles 0.4 - 0.8 GeV |
| S29 | Flux and energy spectrum of primary electrons (1 - 13 GeV) |
| S36 | Solar X-rays 1 - 20 Angstroms |
| S37 | Solar X-rays 44-60 Angstroms |
| S72 | Solar and galactic protons (35 MeV - 1 GeV) and alpha particles (140 - 1200 MeV) |
The satellite carried seven instruments to detect high energy cosmic rays, determine the total flux of solar X-rays, and measure trapped radiation, Van Allen belt protons and cosmic ray protons. There were 2 X-ray instruments: one designed to detect 1-20 Angstroms (consisting of proportional counters with varying window thickness) and one designed to detect 44-60 Angstroms (consisting of proportional counters with thin mylar windows). While geared primarily for solar observations, the detectors are credited with the detection of non-solar X-ray sources.
 Other information
Other information
- The Achievements of ESA Scientific Satellites 1968-1978 ESA SP-1013, April 1979, pp. 6-14.
- Davies, 1997, Astronomy from Space: The Design and Operation of Orbiting Observatories p. 80.
Page authors: Lorella Angelini Jesse Allen
HEASARC Home | Observatories | Archive | Calibration | Software | Tools | Students/Teachers/Public
Last modified: Thursday, 26-Jun-2003 13:48:17 EDT