|
|
OSO-3
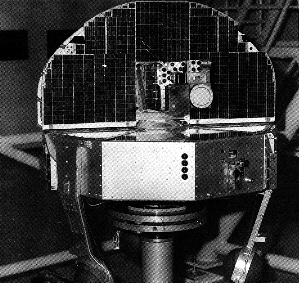
The Third Orbiting Solar Observatory, OSO-3, was launched on 8 March 1967,
into a nearly circular orbit of mean altitude 550 km, inclined at 33
degrees with respect to the equatorial plane. The satellite had two
principle components, a continuously spinning wheel in which the hard X-ray
experiment is mounted with a radial view, and a sail component which
was served to acquire the sun during the orbit day. The attitude control
system maintained the scan plane orientation to within a few degrees of the
sun. The spin-period of the satellite of roughly 1.7 s allowed about 1
cm2/s exposure per revolution to sources on the scan plane. Celestial
sources near the ecliptic plane such as Sco X-1 transited the instrument
scan plane twice a year. Only real-time data were received from the satellite
after the last tape recorder failure on 27 June 1968. The last data transmission
occurred 10 November 1969. OSO-3 descended into the atmosphere on 4 April
1982.
The UCSD X-ray telescope consisted of a single thin NaI(Tl) scintillation
crystal plus phototube assembly enclosed in a howitzer-shaped CsI(Tl)
anti-coincidence shield. The energy resolution was 45 percent at 30 keV.
The instrument operated from 7.7 to 210 keV with 6 channels. The total
effective area was 0.0010 sq-m, but had a 23 deg FWHM field of view. It
scanned the entire sky over the course of the mission.
Also onboard was an MIT gamma-ray instrument. It operated continuously for
about 16 months, at which time the last spacecraft tape recorded failed.
The detector was a counter telescope. The multilayer scintillation detector
consisted of layers of CsI and plastic. The directional Cerenkov counter
was a 3x3 in cylinder of lucite. The energy detector contained several
layers of NaI, sandwiched by layers of tungsten. The entire detector was
enclosed by plastic scintillator detectors. It was sensitive to gamma-rays
above 50 MeV.
The instrument flown on OSO-3 obtained extensive observations of solar
flares, the diffuse component of cosmic X-rays, and the
observation of a single flare episode from Sco X-1.
The gamma-ray instrument registered 621 events attributed to cosmic gamma-
rays above 50 MeV. A complete sky survey showed that the celestial
distribution of gamma-rays is highly anisotropic, being concentrated along
the galactic equator. In addition, an extended region around the galactic
center showed a higher measured intensity.
References
Pelling, R. 1971, Ph.D. dissertation thesis, University of California
(San Diego).
Peterson et al 1966, Phys Rev Let 16, 142.
Peterson et al 1966, ApJ 145, 962.
[Gallery]
[Publications]
[All Missions]
[by Time]
[by Energy]
Page authors: Lorella Angelini Jesse Allen
HEASARC Home |
Observatories |
Archive |
Calibration |
Software |
Tools |
Students/Teachers/Public
Last modified: Thursday, 24-Sep-2020 17:37:05 EDT
|


