



Next: 6.2 Performance of the
Up: 6.1 Description of the
Previous: Filters
There are three software ``switches'' in the WFC which have a
direct influence on the scientific data received from the focal
plane detector.
- Zoom:
- The
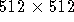 pixel output of the WFC can correspond
to the full
pixel output of the WFC can correspond
to the full 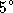 diameter field of view (ZOOM off), or can be
`zoomed' so as to correspond to only the central
diameter field of view (ZOOM off), or can be
`zoomed' so as to correspond to only the central 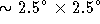 region of the field (ZOOM on). The
angular size of each pixel is therefore halved when the ZOOM is on.
This facility is not normally needed, and has only been used for a
small percentage of observations, mainly during the earlier phases
of the mission.
region of the field (ZOOM on). The
angular size of each pixel is therefore halved when the ZOOM is on.
This facility is not normally needed, and has only been used for a
small percentage of observations, mainly during the earlier phases
of the mission.
- Data rate:
- The on-board storage rate for detected events (i.e.
photons or background particles) is normally restricted to 200 counts
per second. This corresponds to filling the entire WFC allocation of
the on-board tape recorder in 24 hours.
There is a high data rate of 400 counts per second which can be used
for limited periods, for example to take advantage of the storage
allocation not used during intervals when the detector is switched
off (e.g. during radiation belt transits).
The data rate is normally optimised automatically by
on-board software. During the pointed phase of the mission the
detector count rate has rarely exceeded the 200 count per second
threshold during observations. The dead time in the WFC, due primarily
to losses in the queueing of events by the on-board software, depends
on the count rate and which of the two data rates is selected
(Fig. 6.2).
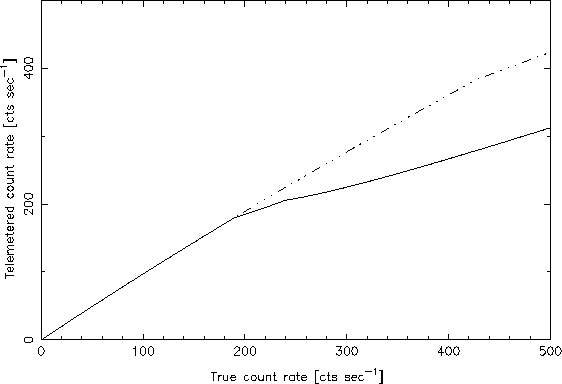
Figure 6.2: Curves showing the telemetered count rate against the true
count rate for the WFC in low speed (solid line) and
high speed telemetry modes (dashed line).
The background count rate in the WFC rarely exceeds
300 counts/s for extended periods of time.
- Electronic windowing:
- This allows the events stored by the WFC
to be restricted to those which are detected within, or outside of,
a restricted spatial window within the field of view of the WFC.
The window can be any rectangular region specified with a resolution
of 32 pixels (i.e. the smallest window possible corresponds to a
region
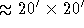 in extent with ZOOM off).
The main use for electronic windowing would be in situations where
the total count rate expected from the whole field of view exceeds
the normal maximum data rate of 200 counts per second (and would
thus lead to large dead times).
Electronic windowing can also be used to `mask out' detector hot-spots
or other defects which would otherwise saturate the data rate;
windowing of such features, which are expected to be essentially fixed,
is achieved within the WFC CDHS using a similar but
independent mechanism.
To date, neither of the windowing facilities has been used.
in extent with ZOOM off).
The main use for electronic windowing would be in situations where
the total count rate expected from the whole field of view exceeds
the normal maximum data rate of 200 counts per second (and would
thus lead to large dead times).
Electronic windowing can also be used to `mask out' detector hot-spots
or other defects which would otherwise saturate the data rate;
windowing of such features, which are expected to be essentially fixed,
is achieved within the WFC CDHS using a similar but
independent mechanism.
To date, neither of the windowing facilities has been used.




Next: 6.2 Performance of the
Up: 6.1 Description of the
Previous: Filters
If you have problems/suggestions please send mail to
rosat_svc@mpe-garching.mpg.de
